Residual solvents in pharmaceuticals are defined as volatile organic chemical substances used or generated in a drug substance or pharmaceutical additive and formulation processes. They are classified for administrative purposes from Class 1 to Class 3 based on their risk to human health.
In the GC-HS method prescribed in the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) General Chapter <467>, Residual Solvents, analysis of solvents must be performed three times for each class. However, using the HS-GCMS method introduced here allows solvents in all three classes to be analyzed in a single measurement. This method also provides qualitative information about unknown peaks.
Due to the mass selectivity offered by GC-MS, the HS-GCMS method achieves quantitation of peaks that cannot be separated sufficiently by GC. A set of chromatograms is shown in Fig. 1. Favorable results were obtained by SIM analysis with repeatability of 1.3 to 3.9 % RSD (Table 1).
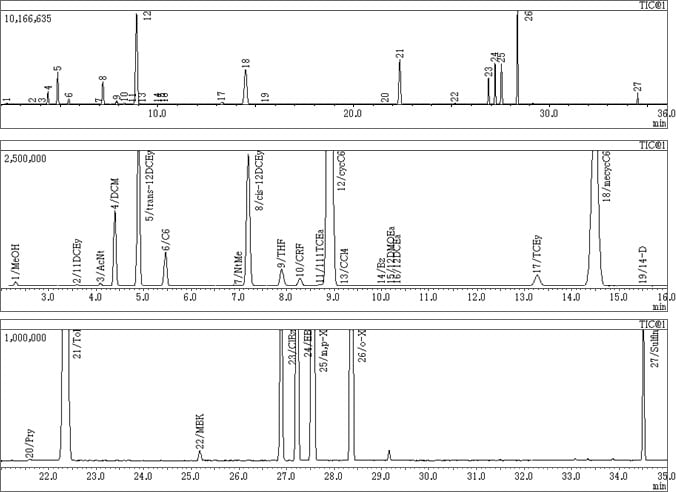
Fig. 1 TIC Chromatogram of 27-Compound Mixture

Volatile components in liquids and solids can be analyzed by using headspace analysis. The term headspace refers to the space atop an object. Constituent compounds with particularly low boiling points are found at the top of liquids and solids. With a headspace sampler, a sample sealed in a vial is heated for a set time so that the sample reaches equilibrium with its gas phase. This gas component (headspace) is then introduced to a gas chromatograph for analysis. Headspace samplers are used to qualitatively and quantitatively analyze aromatic components in foods, components with noxious odors in chemical products, and toxic volatile components in environmental waters.

